Introduction
The Performance-Based Monitoring and Evaluation Framework (PBMEF) is a key component of USAID’s efforts to ensure effective accountability for its investments in TB at global, regional, and country levels to accelerate progress to end the TB epidemic. The Framework, which is fully aligned with existing US and global TB strategies, streamlines and prioritizes indicators for monitoring progress toward reaching global TB milestones and targets in USAID’s 23 TB priority countries. Using the Framework will help national TB programs (NTPs), ministries of health (MOHs), donors, and implementing partners (IPs) with the standardization, analysis, and use of information to inform existing or new TB strategies and interventions, strengthen national monitoring and evaluation (M&E) systems and capacity, and ensure efficient use of resources. The Framework can be used as a tool to advocate for resources, strengthen policies, and expand the scope of collaboration and coordination among partners. Complementing the Framework is a new guide on its use and an online TB Data Hub and Repository, which harness TB data and expand sharing of TB information at global and national levels.
A Guide for TB Programs
The new guide to using the PBMEF, Navigating Tuberculosis Indicators: A Guide for TB Programs, provides an overview of the PBMEF, describes standard core and extended indicators to monitor progress toward reaching TB targets in USAID-supported countries, and encourages consistent use of indicators to monitor and evaluate USAID investments in TB programs. The main intent for this standardized approach is to strengthen the use of data for decision making by the national programs. USAID staff, NTP managers, M&E staff, and embedded TB advisors and IPs are the main audience for this guidance document.
The guide:
- Provides an overview of USAID’s Global Accelerator to End TB and TB targets;
- Explains what the PBMEF is and how it can be used as a data management tool;
- Introduces the performance-based core and extended indicators, along with comprehensive indicator reference sheets for the core indicators and listing of all extended indicators;
- Describes how the indicator data will be reported;
- Provides an overview on data quality; and
- Demonstrates how to view TB data collection through a cascade approach.
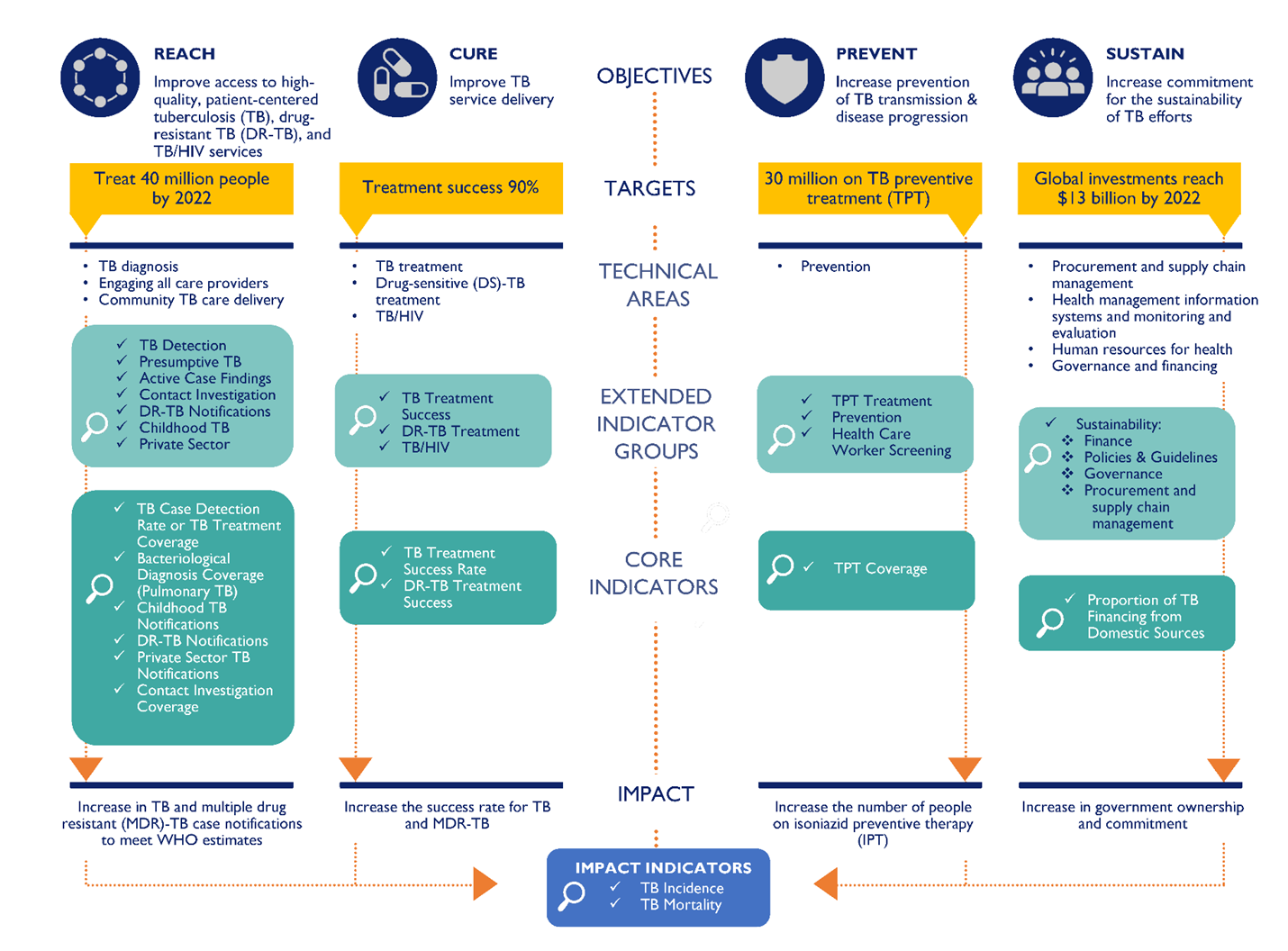
Indicators
A comprehensive list of TB indicators, organized into 14 technical areas, are presented in the Guide. Ten core high-level indicators were selected to best reflect the investments of USAID and the global TB community. They provide a snapshot of a country’s progress toward controlling and eliminating TB in terms of both national and international targets. The core indicators are required reporting for USAID missions, include full indicator reference sheets, and are generally readily available through NTPs’ existing M&E systems or the World Health Organization’s global database. In cases where data are not available at the national level, some additional efforts may be needed to gather data at the subnational level or from IPs.
Additional indicators, referred to as extended indicators, provide more granular data to monitor progress toward the 10 core indicators. These data help to establish potential pathways to anticipated outcomes and are useful for explaining why a country may or may not be achieving its targets, what course corrections may be needed by technical area, and which gaps in programming may require additional resources. The extended indicators can also be used to construct treatment cascades and patient pathways that are critical to understanding where there are gaps and where efforts need to be strengthened.
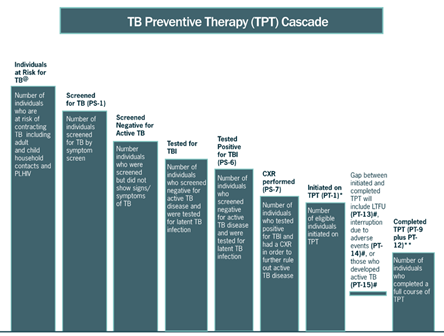
To view the Framework and TB indicators in “Navigating Tuberculosis Indicators: A Guide for TB Programs,” please visit https://www.tbdiah.org/resources/publications/navigating-tuberculosis-indicators-a-guide-for-tb-programs/.
